## Understanding Traits of the Different Generations and Their Characteristics
Navigating the complexities of human interaction often requires understanding the underlying forces that shape individual perspectives and behaviors. One crucial factor is generational affiliation. The **traits of the different generations and their characteristics** offer a powerful lens through which we can analyze societal shifts, workplace dynamics, and even marketing strategies. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the defining traits of each generation, providing you with the knowledge to bridge generational gaps and foster more effective communication. We aim to not only define these traits but also explore their origins, impacts, and relevance in today’s rapidly evolving world. By understanding the unique characteristics of each generation, you can gain a competitive edge in business, build stronger relationships, and navigate the world with greater empathy and insight.
This article goes beyond simple definitions. We’ll explore the historical context, social influences, and technological advancements that have shaped each generation’s worldview. We’ll also examine how these traits manifest in various aspects of life, from work ethic to consumer behavior. Prepare to gain a deeper understanding of the forces that drive generational differences and discover how to harness this knowledge for positive outcomes.
### Why Understanding Generational Traits Matters
Understanding **traits of the different generations and their characteristics** is no longer a nicety; it’s a necessity. In today’s multi-generational workforce, comprehending the values, motivations, and communication styles of different age groups is crucial for effective teamwork and leadership. Moreover, businesses that tailor their marketing strategies to resonate with specific generational cohorts are more likely to succeed. From understanding the financial habits of Baby Boomers to capturing the attention of Gen Z on social media, generational insights are invaluable.
Furthermore, recognizing the distinct characteristics of each generation can foster greater empathy and understanding in our personal lives. By appreciating the experiences and perspectives that have shaped each generation, we can build stronger relationships with family members, friends, and colleagues.
### Article Overview
This article will cover the following key areas:
* **Defining the Generations:** A clear overview of each generation, including their birth years and defining historical events.
* **Core Traits and Characteristics:** An in-depth exploration of the key traits that define each generation, including their values, beliefs, and attitudes.
* **Impact on the Workplace:** How generational differences influence workplace dynamics, communication styles, and leadership approaches.
* **Consumer Behavior:** How each generation approaches spending, brand loyalty, and purchasing decisions.
* **Bridging Generational Gaps:** Strategies for fostering communication, collaboration, and understanding between different generations.
* **Expert Q&A:** Answers to frequently asked questions about generational traits and their implications.
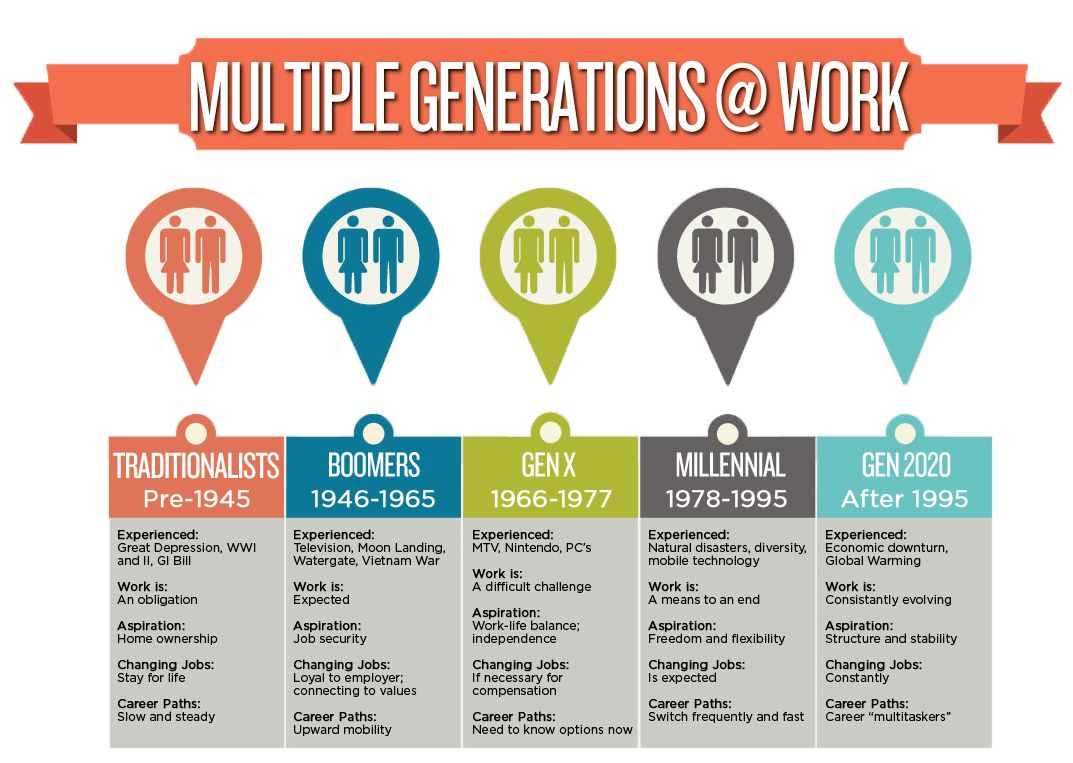
## Defining the Generations: A Quick Overview
Before diving into the specific traits, it’s important to establish a clear understanding of the generations themselves. While birth year ranges can vary slightly depending on the source, here’s a widely accepted breakdown:
* **The Silent Generation (born 1928-1945):** Shaped by the Great Depression and World War II, this generation is known for its hard work, discipline, and respect for authority.
* **Baby Boomers (born 1946-1964):** The product of post-war prosperity, Baby Boomers are often characterized by their optimism, workaholism, and focus on personal achievement.
* **Generation X (born 1965-1980):** Growing up during a time of economic uncertainty and social change, Gen X is known for its independence, resourcefulness, and skepticism.
* **Millennials (born 1981-1996):** Also known as Generation Y, Millennials came of age during the rise of the internet and are characterized by their tech-savviness, social consciousness, and desire for purpose.
* **Generation Z (born 1997-2012):** The first generation to grow up entirely in the digital age, Gen Z is known for its entrepreneurial spirit, diversity, and focus on authenticity.
* **Generation Alpha (born 2013-2025):** The children of Millennials, Generation Alpha is still young, but they are already shaping the future with their digital fluency and global perspective.
## Core Traits and Characteristics: A Deep Dive
Let’s delve into the specific **traits of the different generations and their characteristics**, exploring the values, beliefs, and attitudes that define each cohort.
### The Silent Generation (1928-1945)
* **Key Traits:** Frugality, discipline, respect for authority, loyalty, hard work, delayed gratification.
* **Influences:** The Great Depression, World War II, traditional family values.
* **Characteristics:** This generation values stability, security, and a strong work ethic. They are known for their patriotism, sense of duty, and commitment to institutions. They are often fiscally conservative and prefer to save rather than spend.
### Baby Boomers (1946-1964)
* **Key Traits:** Optimism, workaholism, competitiveness, achievement-oriented, self-reliance.
* **Influences:** Post-war prosperity, the Civil Rights Movement, the Vietnam War, the rise of consumerism.
* **Characteristics:** Baby Boomers are driven by success and recognition. They are often competitive and willing to work long hours to achieve their goals. They value personal growth and are often active participants in social and political causes. They tend to be brand loyal and value quality over price.
### Generation X (1965-1980)
* **Key Traits:** Independence, resourcefulness, skepticism, adaptability, work-life balance.
* **Influences:** Economic uncertainty, rising divorce rates, the AIDS epidemic, the rise of personal computers.
* **Characteristics:** Gen X is known for its pragmatism and self-reliance. They are comfortable with change and are adept at adapting to new technologies. They value work-life balance and are less likely to be defined by their careers than previous generations. They are often skeptical of authority and prefer to make their own decisions.
### Millennials (1981-1996)
* **Key Traits:** Tech-savviness, social consciousness, desire for purpose, collaborative, optimistic.
* **Influences:** The internet, social media, the 9/11 terrorist attacks, the Great Recession.
* **Characteristics:** Millennials are digital natives who are comfortable with technology and social media. They are often socially conscious and driven by a desire to make a positive impact on the world. They value collaboration and teamwork and are looking for purpose in their work. They are often entrepreneurial and willing to take risks.
### Generation Z (1997-2012)
* **Key Traits:** Entrepreneurial spirit, diversity, authenticity, digital fluency, pragmatic.
* **Influences:** Social media, climate change, political polarization, school shootings.
* **Characteristics:** Gen Z is the first generation to grow up entirely in the digital age. They are highly connected and comfortable with technology. They are often entrepreneurial and interested in creating their own businesses. They value diversity and inclusion and are passionate about social and environmental issues. They are pragmatic and realistic about the challenges facing the world.
### Generation Alpha (2013-2025)
* **Key Traits:** Digital fluency, global perspective, tech-dependent, visual learners.
* **Influences:** Technology-driven education, personalized experiences, social media from a young age.
* **Characteristics:** This generation is growing up in a world dominated by technology. They are comfortable with digital devices and are likely to be highly tech-dependent. They are visual learners and respond well to interactive content. They have a global perspective and are aware of issues facing the world.
## Impact on the Workplace: Generational Dynamics
The workplace is increasingly multi-generational, presenting both opportunities and challenges. Understanding how **traits of the different generations and their characteristics** influence workplace dynamics is crucial for effective leadership and teamwork.
* **Communication Styles:** Baby Boomers often prefer face-to-face communication, while Millennials and Gen Z are more comfortable with digital communication. Gen X tends to be direct and to the point.
* **Work Ethic:** The Silent Generation and Baby Boomers often value long hours and dedication to the company, while Gen X, Millennials, and Gen Z prioritize work-life balance.
* **Leadership Styles:** Baby Boomers often prefer hierarchical leadership, while Millennials and Gen Z prefer collaborative and empowering leadership.
* **Training and Development:** Baby Boomers often value traditional training methods, while Millennials and Gen Z prefer online and on-demand learning.
* **Motivation:** Baby Boomers are often motivated by financial security and recognition, while Millennials and Gen Z are motivated by purpose and personal growth.
By understanding these differences, leaders can create a more inclusive and productive workplace that leverages the strengths of each generation. For instance, mentoring programs pairing older and younger employees can facilitate knowledge transfer and build stronger relationships.
## Consumer Behavior: Generational Spending Habits
Each generation has unique spending habits and preferences, influenced by their life experiences and values. Understanding these differences is crucial for businesses targeting specific generational cohorts.
* **The Silent Generation:** This generation is often frugal and value-conscious. They tend to be loyal to brands they trust and are less likely to be swayed by advertising.
* **Baby Boomers:** Baby Boomers have significant purchasing power and are often willing to spend money on quality products and experiences. They are often brand loyal and value customer service.
* **Generation X:** Gen X is often pragmatic and value-oriented. They are less brand loyal than Baby Boomers and are more likely to shop around for the best deals. They are comfortable with online shopping but also value brick-and-mortar stores.
* **Millennials:** Millennials are often experience-driven and value authenticity. They are more likely to spend money on travel, dining, and entertainment. They are highly influenced by social media and are more likely to support brands that align with their values.
* **Generation Z:** Gen Z is highly digital and value-conscious. They are more likely to shop online and are influenced by social media and influencers. They are often looking for deals and discounts and are willing to try new brands.
## Bridging Generational Gaps: Fostering Understanding
Bridging generational gaps requires empathy, understanding, and a willingness to learn from each other. Here are some strategies for fostering communication, collaboration, and understanding between different generations:
* **Encourage Open Communication:** Create a safe space for employees to share their perspectives and experiences, regardless of their age.
* **Promote Mentoring Programs:** Pair older and younger employees to facilitate knowledge transfer and build stronger relationships.
* **Offer Cross-Generational Training:** Provide training on generational differences and communication styles.
* **Recognize and Value Diversity:** Celebrate the unique strengths and contributions of each generation.
* **Embrace Technology:** Utilize technology to facilitate communication and collaboration between different generations.
## Expert Q&A: Addressing Common Questions
Here are some frequently asked questions about **traits of the different generations and their characteristics**:
**Q1: Are generational traits stereotypes?**
While there are common traits associated with each generation, it’s important to remember that these are generalizations, not stereotypes. Individuals within each generation will vary in their beliefs, values, and behaviors.
**Q2: How do cultural differences impact generational traits?**
Cultural differences can significantly influence generational traits. For example, the values and beliefs of Millennials in the United States may differ from those of Millennials in other countries.
**Q3: Are generational labels always accurate?**
Generational labels are not always accurate, as individuals may identify more strongly with one generation than another, regardless of their birth year.
**Q4: How can businesses use generational insights to improve their marketing strategies?**
Businesses can use generational insights to tailor their marketing messages, channels, and product offerings to resonate with specific generational cohorts.
**Q5: How can individuals use generational insights to improve their relationships?**
Individuals can use generational insights to better understand the perspectives and communication styles of people from different generations, fostering empathy and stronger relationships.
**Q6: Do generations evolve over time?**
Yes, generations are not static. As society changes, the traits and characteristics associated with each generation also evolve.
**Q7: What are the key challenges of managing a multi-generational workforce?**
Key challenges include communication barriers, differing work ethics, and varying expectations regarding leadership and management styles.
**Q8: How can I identify which generation someone belongs to?**
While birth year is a primary indicator, consider their life experiences, values, and communication styles to get a better sense of their generational affiliation.
**Q9: Are there any negative consequences of focusing too much on generational differences?**
Overemphasizing generational differences can lead to stereotyping and division. It’s important to focus on individual strengths and contributions rather than making generalizations based on age.
**Q10: How will Generation Alpha impact the future of work and society?**
Generation Alpha, as digital natives and visual learners, is likely to drive innovation in technology, education, and communication, shaping a more connected and personalized future.
## Conclusion: Embracing Generational Diversity
Understanding the **traits of the different generations and their characteristics** is essential for navigating the complexities of modern life. By appreciating the unique perspectives and experiences of each generation, we can foster stronger relationships, build more effective teams, and create a more inclusive society. Remember that generational traits are generalizations, not stereotypes, and that individuals within each generation will vary. Embrace the diversity of perspectives and experiences that each generation brings to the table, and you’ll unlock a wealth of knowledge and innovation.
Now that you have a deeper understanding of generational traits, consider how you can apply this knowledge in your own life. Share your experiences with generational differences in the comments below. Explore our advanced guide to cross-generational communication for more strategies on bridging generational gaps. Contact our experts for a consultation on how to leverage generational insights to improve your business or organization.