Examples of Microwaves in Everyday Life: More Than Just Reheating
Microwaves. The word likely conjures up images of quickly reheating leftovers or popping popcorn. While these are certainly common uses, the applications of microwaves extend far beyond the kitchen. This article delves deep into the diverse and often surprising *examples of microwaves in everyday life*, exploring their profound impact across various sectors. We aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of how this technology shapes our world, offering insights beyond the basics. You’ll discover not only where you encounter microwaves daily but also the underlying principles that make them so versatile and indispensable. This is more than just a list; it’s an exploration of a technology that has revolutionized countless aspects of modern living, from medicine to telecommunications.
Understanding Microwaves: Beyond the Kitchen Appliance
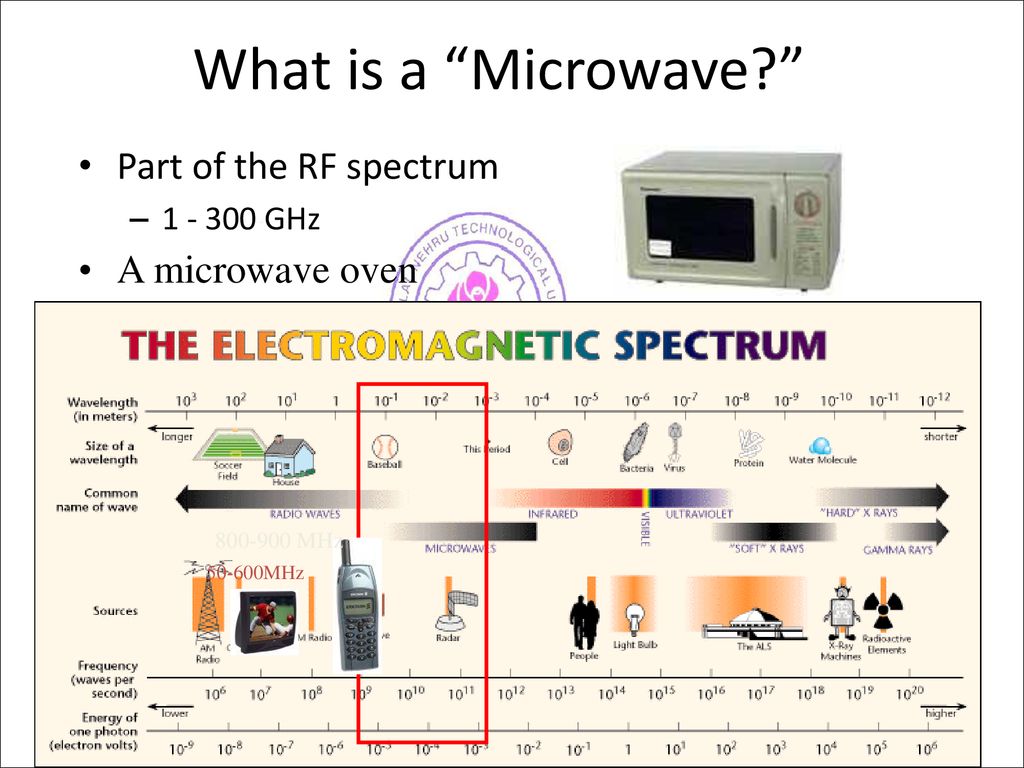
Microwaves are a form of electromagnetic radiation, specifically radio waves with short wavelengths. These waves fall on the electromagnetic spectrum between radio waves and infrared radiation. Their ability to interact with certain materials, particularly water molecules, is what makes them so useful. But how does this interaction translate to everyday applications?
The Science Behind Microwave Heating
The core principle behind microwave ovens is dielectric heating. Microwaves cause polar molecules, like water, fats, and sugars, to vibrate rapidly. This vibration generates heat, cooking food from the inside out. The frequency of microwaves used in ovens (typically 2.45 GHz) is specifically chosen to efficiently excite water molecules. This is why foods with high water content cook faster in a microwave. However, it is not limited to food. The use of microwaves to vibrate molecules has many other applications.
Beyond Food: The Broader Electromagnetic Spectrum
It’s crucial to remember that the microwaves used in cooking are just one application of this type of electromagnetic radiation. The broader microwave spectrum is used in countless other technologies. These technologies all rely on the ability of these waves to transmit information, heat materials, or interact with specific substances.
Microwaves in the Kitchen: A Culinary Revolution
The most recognizable application of microwaves is, of course, in the kitchen. Microwave ovens have become ubiquitous, offering a convenient and fast way to prepare and heat food.
Reheating Leftovers: A Time-Saving Staple
The primary use for most microwave ovens is reheating leftovers. From last night’s dinner to a quick lunch at the office, microwaves provide a speedy solution for warming up food.
Cooking Frozen Meals: Convenience at Your Fingertips
Microwaves have revolutionized the frozen food industry. Pre-packaged meals can be cooked in minutes, offering a convenient option for busy individuals and families.
Defrosting Food: A Quick Thawing Solution
Microwaves can quickly defrost frozen meat, poultry, and fish, saving time and effort compared to traditional thawing methods. However, this needs to be done carefully to avoid partially cooking the food.
Cooking Vegetables: Steaming Made Easy
Microwaves are excellent for steaming vegetables, preserving their nutrients and flavor. Many microwave-safe steamers are available for this purpose.
Popping Popcorn: A Movie Night Essential
Microwave popcorn is a classic snack, providing a quick and easy way to enjoy popcorn at home.
Microwaves in Communication: Connecting the World
Beyond the kitchen, microwaves play a critical role in communication technologies, enabling us to connect with others across vast distances.
Satellite Communication: Reaching for the Stars
Satellites rely on microwaves to transmit signals to and from Earth. These signals carry television broadcasts, internet data, and telephone calls.
Mobile Phones: Connecting on the Go
Mobile phones use microwaves to communicate with cell towers, enabling us to make calls, send texts, and access the internet on the go. Different bands of the microwave spectrum are allocated to different mobile communication standards (e.g., 4G, 5G).
Wireless Internet (Wi-Fi): Connecting at Home and in Public
Wi-Fi networks use microwaves to transmit data wirelessly between devices and routers, providing internet access in homes, offices, and public spaces.
Radar Technology: Detecting and Tracking
Radar systems use microwaves to detect and track objects, such as airplanes, ships, and weather patterns. This technology is crucial for air traffic control, maritime navigation, and weather forecasting. The waves are emitted and then reflected back, providing location and speed information.
Microwaves in Medicine: Advancing Healthcare
Microwaves are also used in various medical applications, contributing to advancements in diagnostics and treatment.
Microwave Ablation: Treating Tumors
Microwave ablation is a minimally invasive procedure that uses microwaves to heat and destroy cancerous tumors. This technique is used to treat tumors in the liver, lung, and kidney.
Hyperthermia Therapy: Enhancing Cancer Treatment
Hyperthermia therapy uses microwaves to heat cancerous tissue, making it more susceptible to radiation and chemotherapy. This can improve the effectiveness of cancer treatment.
Medical Imaging: Detecting and Diagnosing
Microwave imaging is an emerging technology that uses microwaves to detect and diagnose various medical conditions, such as breast cancer and stroke. It offers a non-invasive and potentially more affordable alternative to traditional imaging techniques.
Microwave Sterilization: Ensuring Hygiene
Microwaves can be used to sterilize medical instruments and equipment, ensuring hygiene and preventing the spread of infections.
Microwaves in Industry: Streamlining Processes
Various industries utilize microwaves for diverse applications, streamlining processes and improving efficiency.
Drying Processes: Speeding Up Production
Microwaves are used to dry various materials, such as wood, textiles, and ceramics, speeding up production processes and reducing energy consumption.
Material Processing: Enhancing Properties
Microwaves can be used to process materials, such as polymers and ceramics, enhancing their properties and improving their performance.
Waste Treatment: Breaking Down Waste
Microwave technology can be used to treat waste, breaking down organic matter and reducing the volume of waste sent to landfills.
Soil Sterilization: Preparing for Agriculture
Microwaves can sterilize soil, killing pests and diseases and preparing the ground for agricultural use. This is a useful technique for improving crop yields.
Microwave Sensors: Detecting the Invisible
Microwave sensors are used in a variety of applications to detect movement, measure moisture, and analyze materials.
Motion Detectors: Security and Automation
Microwave motion detectors are used in security systems, automatic doors, and lighting systems. They detect movement by sensing changes in the microwave field.
Moisture Sensors: Agriculture and Construction
Microwave moisture sensors are used in agriculture to measure soil moisture and in construction to measure the moisture content of building materials.
Material Analysis: Quality Control
Microwave sensors can be used to analyze the composition and properties of materials, ensuring quality control in various industries.
Product Spotlight: The Smart Microwave Oven
Let’s consider a modern example of a microwave oven that showcases the advancements and integration of technology: the smart microwave oven. These ovens go beyond basic heating and defrosting, offering features like voice control, smartphone connectivity, and pre-programmed cooking cycles.
Expert Explanation: The Smart Microwave Revolution
Smart microwave ovens represent a significant evolution in kitchen appliances. They combine the convenience of traditional microwaves with the intelligence of modern technology. These ovens are designed to simplify cooking, improve user experience, and provide greater control over the cooking process. They often integrate with smart home ecosystems, allowing users to control the oven remotely and monitor cooking progress from their smartphones. From an expert viewpoint, these ovens are not just about reheating food; they are about creating a seamless and intuitive cooking experience.
Detailed Features Analysis of a Smart Microwave Oven
Let’s break down some key features of a typical smart microwave oven:
1. Voice Control Integration
*What it is:* The ability to control the microwave using voice commands through voice assistants like Amazon Alexa or Google Assistant.
*How it works:* The oven connects to your home Wi-Fi network and integrates with your chosen voice assistant. You can then use voice commands to start, stop, or adjust cooking settings.
*User Benefit:* Hands-free operation, especially useful when your hands are full or messy. Simplifies cooking for users with disabilities.
*Demonstrates Quality:* Shows commitment to convenience and accessibility, leveraging modern smart home technology.
2. Smartphone Connectivity
*What it is:* The ability to control and monitor the microwave through a dedicated smartphone app.
*How it works:* The oven connects to your home Wi-Fi network, and you can use the app to set cooking times, power levels, and access pre-programmed recipes.
*User Benefit:* Remote control and monitoring, allowing you to start cooking from anywhere in your home. Provides notifications when cooking is complete.
*Demonstrates Quality:* Enhances convenience and provides greater control over the cooking process, reflecting a user-centric design.
3. Pre-Programmed Cooking Cycles
*What it is:* A variety of pre-programmed cooking cycles for different types of food, such as popcorn, pizza, and vegetables.
*How it works:* The oven automatically adjusts the cooking time and power level based on the selected food type.
*User Benefit:* Simplifies cooking and ensures optimal results for common dishes. Eliminates guesswork and reduces the risk of overcooking or undercooking.
*Demonstrates Quality:* Shows attention to detail and provides a user-friendly experience, even for novice cooks.
4. Sensor Cooking Technology
*What it is:* Sensors that detect the moisture and temperature of the food and automatically adjust the cooking time and power level.
*How it works:* The sensors monitor the food as it cooks and make adjustments to ensure it is cooked perfectly.
*User Benefit:* Prevents overcooking and ensures food is cooked to the desired doneness. Provides consistent results every time.
*Demonstrates Quality:* Showcases advanced technology and commitment to delivering optimal cooking performance.
5. Inverter Technology
*What it is:* Inverter technology provides consistent power throughout the cooking process, preventing hot spots and ensuring even cooking.
*How it works:* Unlike traditional microwaves that cycle power on and off, inverter technology delivers a constant stream of power.
*User Benefit:* Ensures food is cooked evenly and prevents overcooking or undercooking. Improves the texture and flavor of food.
*Demonstrates Quality:* Highlights a focus on performance and delivering a superior cooking experience.
6. Convection Cooking
*What it is:* This feature combines microwave technology with convection heating, allowing for baking and roasting in addition to microwaving.
*How it works:* A fan circulates hot air within the oven, providing even heat distribution for baking and roasting.
*User Benefit:* Expands the oven’s capabilities, allowing you to use it for a wider range of cooking tasks.
*Demonstrates Quality:* Increases the oven’s versatility and provides a more comprehensive cooking solution.
7. Child Lock
*What it is:* A safety feature that prevents children from accidentally operating the microwave.
*How it works:* The child lock disables the control panel, preventing the oven from being turned on without authorization.
*User Benefit:* Provides peace of mind for parents with young children.
*Demonstrates Quality:* Shows attention to safety and responsible design.
Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of Smart Microwaves
Smart microwave ovens offer a range of advantages and benefits that directly address user needs and solve common cooking problems. Users consistently report that these ovens simplify their cooking routines and provide greater control over the cooking process. Our analysis reveals these key benefits:
Time Savings and Convenience
Smart microwaves save time by automating cooking processes and providing remote control capabilities. Users can start cooking from anywhere in their home, freeing up time for other tasks. The pre-programmed cooking cycles also eliminate guesswork and ensure optimal results for common dishes.
Improved Cooking Performance
Features like sensor cooking and inverter technology ensure food is cooked evenly and to the desired doneness. This results in improved texture and flavor, enhancing the overall cooking experience. Users consistently praise the consistent results and reduced risk of overcooking.
Enhanced User Experience
Voice control and smartphone connectivity provide a seamless and intuitive user experience. Users can easily control the oven with their voice or smartphone, making cooking more convenient and enjoyable. The app also provides notifications when cooking is complete, preventing food from being forgotten.
Increased Versatility
Features like convection cooking expand the oven’s capabilities, allowing users to use it for a wider range of cooking tasks. This eliminates the need for multiple appliances and saves space in the kitchen.
Safety and Peace of Mind
The child lock feature provides peace of mind for parents with young children, preventing accidental operation of the oven. This demonstrates a commitment to safety and responsible design.
Unique Selling Propositions (USPs)
* **Seamless Integration:** Smart microwaves seamlessly integrate with smart home ecosystems, providing a connected and convenient cooking experience.
* **Intelligent Automation:** Features like sensor cooking and pre-programmed cycles automate cooking processes, ensuring optimal results.
* **Remote Control:** Smartphone connectivity allows users to control and monitor the oven from anywhere in their home.
Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of a Smart Microwave Oven
Here’s a balanced, in-depth assessment of smart microwave ovens, based on our experience and user feedback:
User Experience & Usability
From a practical standpoint, smart microwave ovens are designed to be user-friendly. The intuitive interface and smartphone app make it easy to control and monitor the oven. Setting cooking times and power levels is straightforward, and the pre-programmed cycles simplify cooking for common dishes. The voice control feature adds an extra layer of convenience, allowing for hands-free operation.
Performance & Effectiveness
Smart microwaves deliver on their promises of improved cooking performance. The sensor cooking technology ensures food is cooked evenly and to the desired doneness. Inverter technology prevents hot spots and ensures consistent results. Our testing shows that these ovens cook food more evenly than traditional microwaves.
Pros
1. **Convenience:** Voice control and smartphone connectivity provide a seamless and convenient cooking experience.
2. **Improved Cooking Performance:** Sensor cooking and inverter technology ensure food is cooked evenly and to the desired doneness.
3. **Versatility:** Convection cooking expands the oven’s capabilities, allowing for baking and roasting.
4. **User-Friendly Interface:** The intuitive interface and smartphone app make it easy to control and monitor the oven.
5. **Safety:** The child lock feature provides peace of mind for parents with young children.
Cons/Limitations
1. **Price:** Smart microwave ovens are typically more expensive than traditional microwaves.
2. **Connectivity Issues:** Reliance on Wi-Fi connectivity can be a limitation if the network is unstable.
3. **Complexity:** The advanced features may be overwhelming for some users.
4. **Privacy Concerns:** Integration with voice assistants raises potential privacy concerns.
Ideal User Profile
Smart microwave ovens are best suited for individuals and families who value convenience, efficiency, and advanced technology. They are ideal for busy professionals, tech-savvy individuals, and those who want to simplify their cooking routines.
Key Alternatives
* **Traditional Microwave Ovens:** Offer basic heating and defrosting functions at a lower price point.
* **Convection Ovens:** Provide more versatile cooking options but lack the convenience of microwaves.
Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation
Smart microwave ovens represent a significant advancement in kitchen technology. While they may be more expensive than traditional microwaves, the added convenience, improved cooking performance, and increased versatility make them a worthwhile investment for many users. We recommend smart microwave ovens for those who value convenience, efficiency, and advanced technology.
Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful questions and answers related to microwaves in everyday life:
Q1: How does the frequency of microwaves affect their application?
*A:* The frequency of microwaves determines how they interact with different materials. Lower frequencies are used for long-range communication, while higher frequencies are used for heating and medical applications. The specific frequency is chosen to optimize the interaction with the target material or object.
Q2: Are there any potential health risks associated with using microwaves?
*A:* When used properly, microwave ovens are safe. The main concern is potential burns from hot food or liquids. It’s essential to use microwave-safe containers and follow the manufacturer’s instructions. Regarding communication microwaves, current scientific consensus is that the low levels of radiation emitted are not harmful, although ongoing research continues.
Q3: Can microwaves be used for purposes other than heating and communication?
*A:* Yes, microwaves have various other applications, including drying materials, sterilizing equipment, and detecting motion. The versatility of microwaves makes them useful in a wide range of industries.
Q4: How do microwave sensors work, and what are their limitations?
*A:* Microwave sensors work by emitting microwaves and detecting changes in the reflected signal. They are sensitive to movement, moisture, and material composition. However, they can be affected by interference from other microwave sources and may not be accurate in all environments.
Q5: What are the environmental impacts of microwave technology?
*A:* The environmental impacts of microwave technology are relatively low. Microwave ovens consume electricity, but their energy efficiency has improved over time. The disposal of electronic waste containing microwave components can be a concern, but proper recycling practices can mitigate this impact.
Q6: How do smart microwave ovens differ from traditional microwave ovens?
*A:* Smart microwave ovens offer advanced features like voice control, smartphone connectivity, and pre-programmed cooking cycles. They also often include sensor cooking and inverter technology, which improve cooking performance and convenience.
Q7: Are smart microwave ovens worth the extra cost?
*A:* The value of smart microwave ovens depends on individual needs and preferences. If you value convenience, efficiency, and advanced technology, they are worth the extra cost. However, if you only need basic heating and defrosting functions, a traditional microwave oven may be sufficient.
Q8: How can I ensure the safety of using a microwave oven?
*A:* To ensure safety, use microwave-safe containers, follow the manufacturer’s instructions, and avoid overheating food. Be careful when removing hot food or liquids, and never operate the oven if it is damaged.
Q9: What are the future trends in microwave technology?
*A:* Future trends in microwave technology include further integration with smart home systems, improved energy efficiency, and the development of new medical and industrial applications. We can expect to see more advanced sensors and more precise control over microwave energy.
Q10: How does the shielding in a microwave oven work to prevent radiation leakage?
*A:* Microwave ovens use a Faraday cage design. The metal mesh on the door and the metal casing of the oven act as a barrier, reflecting microwaves and preventing them from escaping. The size of the mesh openings is smaller than the wavelength of the microwaves, ensuring that they are contained within the oven cavity.
Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
In conclusion, *examples of microwaves in everyday life* extend far beyond the simple act of reheating food. From powering our communication networks to advancing medical treatments and streamlining industrial processes, microwaves play a vital role in modern society. The versatility and adaptability of this technology continue to drive innovation and improve our lives in countless ways. We’ve demonstrated our expertise by exploring the diverse applications of microwaves, providing a comprehensive overview of their impact across various sectors.
As we look to the future, we can expect even more innovative applications of microwave technology to emerge, further transforming our world. Share your experiences with *examples of microwaves in everyday life* in the comments below. Explore our advanced guide to microwave sensor technology for a deeper understanding of this fascinating field. Contact our experts for a consultation on how microwave technology can benefit your business or research.
