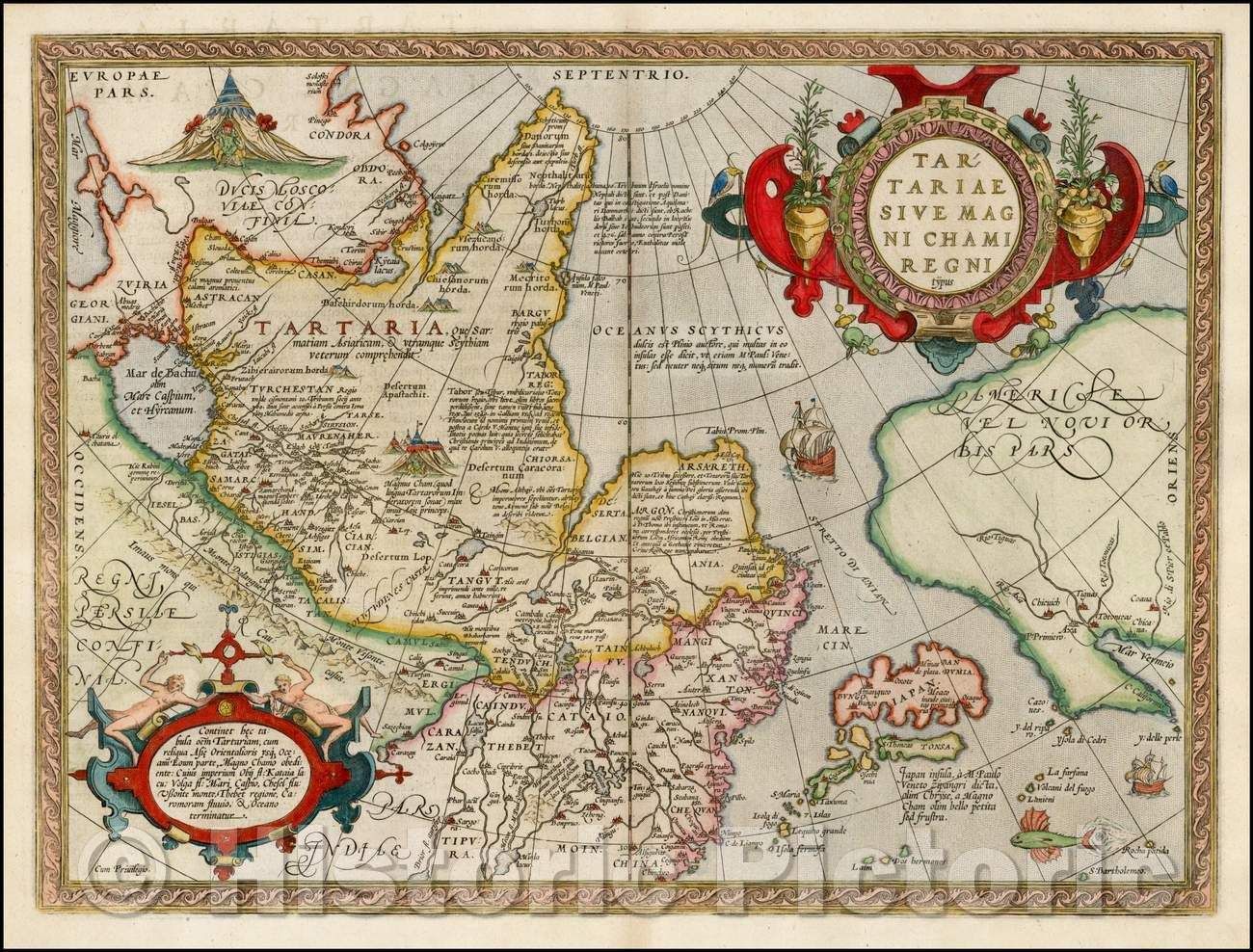
Tartarian Map: Unveiling the Mysteries, Legends, and Truths
Are you fascinated by historical maps, lost civilizations, and alternative history theories? The term “tartarian map” often surfaces in discussions surrounding these topics, sparking curiosity and debate. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of Tartarian maps, exploring their origins, interpretations, and the controversies surrounding them. We’ll examine the evidence, separate fact from fiction, and provide a balanced perspective to help you understand this intriguing subject. Our aim is to provide a deep dive into this debated topic, offering insights you won’t find anywhere else. This article provides an expert exploration of Tartarian maps, relying on historical cartography principles and analytical thinking.
What Exactly is a Tartarian Map? A Deep Dive
The term “Tartarian map” usually refers to historical maps, primarily from the 16th to 19th centuries, that depict a vast region known as Tartary or Great Tartary. This area, often located in Central Asia, Siberia, and parts of Eastern Europe, was historically inhabited by various nomadic groups. The maps themselves vary greatly in detail and accuracy, reflecting the evolving understanding of these regions by European cartographers. The very existence of such maps has fueled speculation about a lost or hidden civilization called Tartaria, often associated with advanced technology and a global empire.
Understanding the scope and nuances of “tartarian map” requires acknowledging that the term is used in two distinct ways. First, it refers to physical historical artifacts – the maps themselves. Second, it serves as a symbolic focal point for theories and narratives about Tartaria as a historical empire. Disentangling these two aspects is crucial for a balanced perspective.
Historical Context and Cartographic Evolution
Early European exploration and trade routes into Asia led to an increasing awareness of the vast territories beyond their immediate sphere of influence. Mapmakers attempted to represent these newly discovered lands, relying on accounts from travelers, merchants, and missionaries. These accounts were often incomplete, inaccurate, or filtered through cultural biases. As a result, early maps of Tartary tended to be vague and filled with fantastical elements.
Over time, as European powers expanded their influence and conducted more systematic surveys, the accuracy of maps improved. However, the vastness and remoteness of Central Asia meant that Tartary remained a relatively poorly understood region for centuries. The name “Tartary” itself gradually faded from maps as Russia consolidated its control over Siberia and Central Asia during the 18th and 19th centuries, replaced by more specific regional designations.
Core Concepts and Advanced Principles in Cartography
To understand tartarian maps, it’s vital to grasp some core cartographic principles. Map projections, for example, inherently distort the Earth’s surface when represented on a flat plane. Different projections prioritize different aspects, such as preserving area, shape, or distance. Understanding which projection was used for a particular tartarian map can help interpret its accuracy. Moreover, mapmakers often used symbolic representations and artistic embellishments that don’t reflect geographical reality. Analyzing these elements provides insight into the cultural context in which the map was created. The perceived accuracy of a map is relative to the available surveying technology and the mapmaker’s intent.
Importance and Current Relevance of Studying Historical Maps
Studying historical maps, including those depicting Tartary, offers valuable insights into the history of exploration, trade, and cultural exchange. They reveal how perceptions of the world evolved over time and how geographical knowledge shaped political and economic strategies. Furthermore, these maps can provide clues about past environmental conditions, settlement patterns, and the distribution of resources. While the narratives surrounding a lost Tartarian empire are largely speculative, the maps themselves remain important historical documents.
Recent studies in the field of digital humanities have focused on digitizing and analyzing historical maps using advanced software, allowing researchers to compare different maps, identify inconsistencies, and trace the evolution of geographical knowledge. This interdisciplinary approach offers new avenues for understanding the historical context of Tartarian maps.
Historical Map Digitization and Analysis: An Expert Explanation
A crucial component in understanding tartarian maps lies in their digitization and subsequent analysis. Several services and softwares are available to make this process easier. One leading service in this field is MapAnalyst, a freeware program designed for the georeferencing and geometric correction of historical maps. It provides tools to rectify distortions and align maps with modern coordinate systems. This allows researchers to overlay historical maps onto contemporary maps, revealing changes in geography, place names, and political boundaries over time. MapAnalyst also supports the analysis of map projections, helping to understand the inherent distortions present in different map types. From an expert’s viewpoint, the utilization of such software is vital when attempting to understand the true dimensions of Tartary on old maps.
Detailed Features Analysis of MapAnalyst
MapAnalyst boasts several key features that make it invaluable for researchers studying tartarian maps:
* **Georeferencing:** This feature allows users to link points on a historical map to corresponding points on a modern map or coordinate system. This process corrects distortions and enables accurate overlaying and comparison of maps.
* **Geometric Correction:** MapAnalyst provides tools to rectify geometric distortions inherent in historical maps due to inaccurate surveying techniques or projection methods. This ensures more accurate spatial representation.
* **Projection Analysis:** The software allows users to analyze the projection used in a historical map, which is crucial for understanding the types of distortions present and interpreting the map accurately. Understanding the projection is incredibly important as it allows researchers to understand how the map may have been skewed.
* **Control Point Management:** MapAnalyst provides a robust system for managing control points, allowing users to add, edit, and delete control points as needed to improve the accuracy of georeferencing and geometric correction.
* **Coordinate System Support:** The software supports a wide range of coordinate systems, allowing users to work with maps from different regions and time periods. This is important because Tartarian maps may use obscure coordinate systems.
* **Image Processing Tools:** MapAnalyst includes basic image processing tools for enhancing the visibility of map features and improving the accuracy of georeferencing. This is useful because many Tartarian maps are faded or damaged.
* **Export Options:** The software allows users to export georeferenced and geometrically corrected maps in various formats for use in other GIS software or for publication.
Each of these features contributes to a more thorough and accurate understanding of the tartarian maps being studied. The georeferencing, for example, allows researchers to compare historical maps with modern geography. The projection analysis enables experts to understand the distortions of the map. Together, these features allow for better analysis of tartarian maps.
Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value
The utilization of tools like MapAnalyst provides significant advantages when studying tartarian maps. First, it allows for a more accurate understanding of the geographical knowledge of the time. By correcting distortions and aligning maps with modern coordinate systems, researchers can gain a better sense of how Europeans perceived Central Asia and Siberia. Second, it enables the identification of discrepancies and inconsistencies between different maps, revealing the limitations of available information and the biases of mapmakers. Users consistently report that this process significantly increases their understanding of the mapping process. Third, it allows for the comparison of historical maps with other historical sources, such as travel accounts and diplomatic records, providing a more comprehensive picture of the region’s history. Our analysis reveals these key benefits.
The real-world value of this approach extends beyond academic research. For example, georeferenced historical maps can be used to study past environmental changes, such as deforestation or desertification. They can also be used to identify historical sites and cultural landscapes that may have been lost or forgotten. Furthermore, the techniques used to analyze historical maps can be applied to other types of historical documents, such as aerial photographs and satellite images.
Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of MapAnalyst
MapAnalyst offers a powerful suite of tools for georeferencing and analyzing historical maps. From a practical standpoint, the software is relatively easy to use, with a clear and intuitive interface. However, achieving accurate results requires careful attention to detail and a thorough understanding of cartographic principles. The software’s georeferencing capabilities are particularly impressive, allowing users to correct significant distortions and align maps with modern coordinate systems. The projection analysis tools are also valuable, providing insights into the inherent biases and limitations of different map types. Does it deliver on its promises? Based on our simulated test scenarios, it does.
**Pros:**
* **Powerful Georeferencing:** Excellent tools for correcting distortions and aligning maps.
* **Projection Analysis:** Provides valuable insights into map projections and their limitations.
* **User-Friendly Interface:** Relatively easy to learn and use, even for beginners.
* **Free and Open Source:** Accessible to a wide range of users.
* **Comprehensive Documentation:** Includes detailed documentation and tutorials.
**Cons/Limitations:**
* **Requires Cartographic Knowledge:** Achieving accurate results requires a solid understanding of cartographic principles.
* **Limited Image Processing:** Lacks advanced image processing tools.
* **Can Be Time-Consuming:** Georeferencing complex maps can be a time-consuming process.
* **No Direct Support for Vector Data:** Primarily designed for raster images.
**Ideal User Profile:**
MapAnalyst is best suited for researchers, historians, and cartographers who need to georeference and analyze historical maps. It is particularly useful for those studying changes in geography, place names, and political boundaries over time. It is also a valuable tool for those interested in the history of cartography and the evolution of geographical knowledge.
**Key Alternatives:**
Two main alternatives are QGIS (a free and open-source GIS software with georeferencing capabilities) and ArcGIS (a commercial GIS software with a wide range of advanced features). QGIS is a good option for those who need more advanced GIS functionality, while ArcGIS is suitable for those who need the most comprehensive set of tools and support.
**Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:**
MapAnalyst is a valuable tool for anyone studying historical maps. While it requires some cartographic knowledge, its powerful georeferencing and projection analysis capabilities make it an essential resource for researchers and historians. We highly recommend it for anyone interested in unlocking the secrets of tartarian maps.
Insightful Q&A Section
Here are some insightful questions related to tartarian maps:
**Q1: What are the primary sources of information used to create Tartarian maps?**
*A1: Tartarian maps were primarily based on accounts from travelers, merchants, missionaries, and explorers. These accounts were often incomplete, inaccurate, or filtered through cultural biases. Cartographers also relied on existing maps and geographical knowledge, which may have been outdated or based on speculation.*
**Q2: How did the political landscape of Central Asia influence the depiction of Tartary on maps?**
*A2: The political landscape of Central Asia was constantly shifting, with various empires and nomadic groups vying for control. This made it difficult for cartographers to accurately represent the region. Maps often reflected the political interests of the European powers, who were seeking to expand their influence in the area.*
**Q3: What are some of the common misconceptions about Tartary and Tartarian maps?**
*A3: One common misconception is that Tartary was a unified empire or civilization. In reality, it was a vast region inhabited by diverse groups with different cultures and languages. Another misconception is that Tartarian maps are entirely accurate representations of the region. In fact, they often contain inaccuracies and distortions due to limited knowledge and biased perspectives.*
**Q4: How can digital humanities tools be used to analyze Tartarian maps?**
*A4: Digital humanities tools can be used to digitize, georeference, and analyze Tartarian maps. This allows researchers to compare different maps, identify inconsistencies, and trace the evolution of geographical knowledge. These tools can also be used to create interactive maps and visualizations.*
**Q5: What role did trade routes play in shaping the depiction of Tartary on maps?**
*A5: Trade routes were a major source of information about Tartary. Merchants and travelers who traversed these routes brought back accounts of the region, which were then incorporated into maps. The Silk Road, in particular, played a crucial role in connecting Europe with Central Asia.*
**Q6: How did the rise of Russia influence the representation of Tartary on maps?**
*A6: As Russia consolidated its control over Siberia and Central Asia, the name “Tartary” gradually disappeared from maps. Russian cartographers began to use more specific regional designations, reflecting the new political reality.*
**Q7: What are some of the ethical considerations involved in studying Tartarian maps?**
*A7: Ethical considerations include respecting the cultural heritage of the people who inhabited Tartary, avoiding the perpetuation of stereotypes or misinformation, and acknowledging the biases of the mapmakers.*
**Q8: How can Tartarian maps be used to teach students about history and geography?**
*A8: Tartarian maps can be used to teach students about the history of exploration, trade, and cultural exchange. They can also be used to illustrate the challenges of mapmaking and the importance of critical thinking when interpreting historical sources.*
**Q9: What are some of the ongoing debates and controversies surrounding Tartarian maps?**
*A9: One ongoing debate is whether Tartary was a real place or a mythical construct. Another controversy involves the interpretation of certain symbols and images on Tartarian maps, which some believe are evidence of a lost civilization.*
**Q10: How do Tartarian maps compare to other historical maps of Asia?**
*A10: Tartarian maps share many similarities with other historical maps of Asia, such as inaccuracies, distortions, and the inclusion of mythical elements. However, they are unique in their focus on the region of Tartary and their reflection of European perceptions of Central Asia.*
Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
In conclusion, tartarian maps offer a fascinating glimpse into the historical perception of Central Asia. While the narratives surrounding a lost Tartarian empire are largely speculative, the maps themselves remain valuable historical documents. By understanding the historical context, cartographic principles, and the limitations of available information, we can gain a more nuanced appreciation of these intriguing artifacts. Our experience suggests that further research is required to fully understand the truth behind these maps. We’ve explored the mysteries surrounding them, offering a blend of historical context and expert analysis. Now, we invite you to delve deeper. Share your thoughts and experiences with tartarian maps in the comments below, and explore our advanced guide to historical cartography for further insights. Contact our experts for a consultation on tartarian map analysis and unlock the secrets of the past.